Jagadish Chandra Bose | Inventions, Education, & Biography.
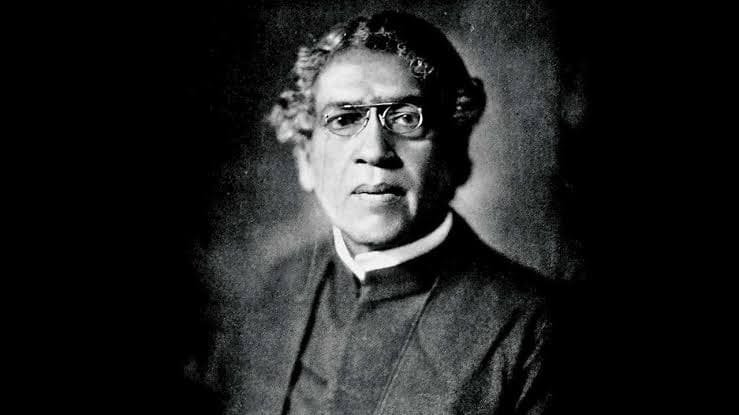
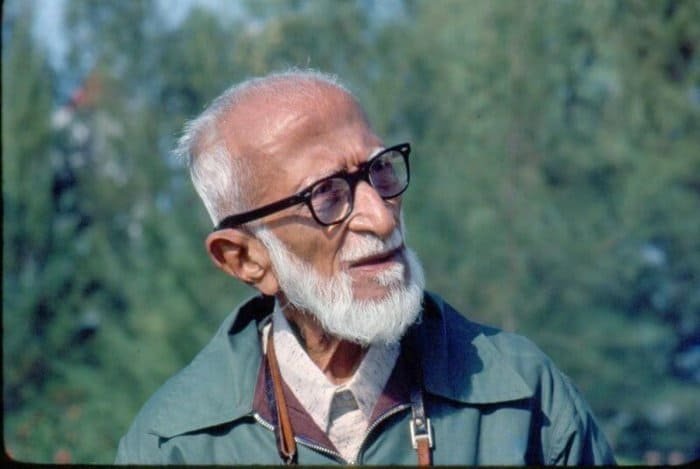
Sir Jagadish Chandra Bose (1858–1937) was a remarkable Indian scientist, polymath, and visionary. His contributions spanned multiple disciplines, including biology, physics, and botany. Let’s delve into the life and achievements of this extraordinary individual.
Quick Inormation
- Birth: November 30, 1858, in Mymensingh, Bengal, India (now in Bangladesh).
- Death: November 23, 1937, in Giridih, Bihar (aged 78).
- Subjects of Study:
- Stimulus-Response Behavior: Bose demonstrated that both animals and plants share much in common. He proved that plants are sensitive to heat, cold, light, noise, and various other external stimuli.
- Scientific Contributions:
- Radio Waves and Coherer:
- Bose’s experiments on the quasi-optical properties of very short radio waves (1895) led to improvements in the coherer, an early form of radio detector. These contributions influenced the development of solid-state physics.
- Plant Physiology:
- He invented the crescograph, a device for measuring plant growth.
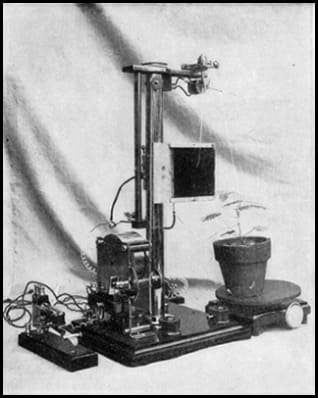
- Demonstrated an apparent power of feeling in plants by observing their responses to stimuli, exemplified by the quivering of injured plants.
- Bose Institute:
- Founded the Bose Institute in Calcutta (now Kolkata) in 1917, Asia’s first interdisciplinary research center.
- Served as the Director of Bose Institute from its inception until his death.
- Radio Waves and Coherer:
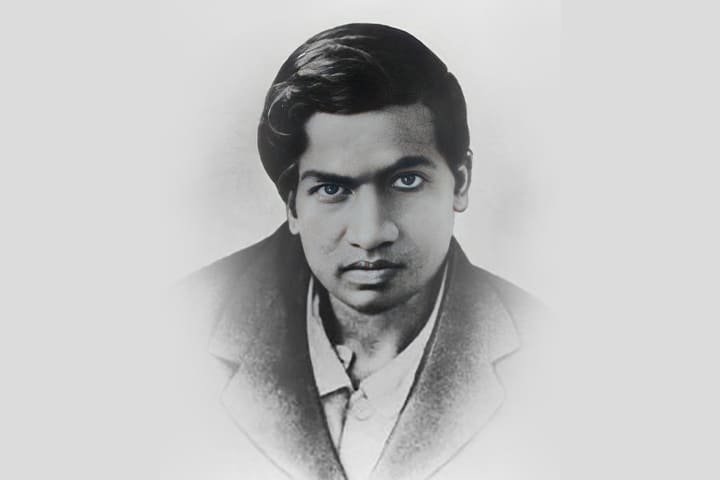
Early Life and Education
- Born on November 30, 1858, in Bikrampur, Bengal Presidency (now part of Bangladesh), Bose attended Dhaka Collegiate School before pursuing higher education.
- He graduated from St. Xavier’s College, Calcutta (now Kolkata) and later studied at the University of London. Unfortunately, health issues forced him to abandon his medical studies.
Pioneering Research
- Radio Waves and Coherer:
- Bose conducted groundbreaking experiments on radio waves in the microwave spectrum.
- His work led to improvements in the coherer, an early radio detector, contributing to the development of solid-state physics.
- Plant Physiology:
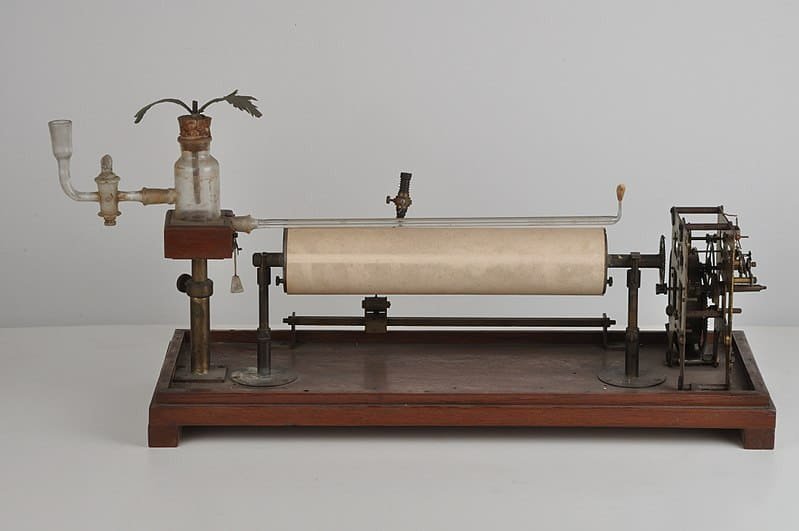

- Bose invented the crescograph, a device for measuring plant growth.
- He demonstrated that plants exhibit a form of feeling by observing their responses to stimuli.
- His books, such as Response in the Living and Non-Living (1902), explored these phenomena.
Legacy and Honors
- Considered the father of Bengali science fiction, Bose blended scientific rigor with imaginative storytelling.
- He founded the Bose Institute in 1917, Asia’s first interdisciplinary research center.
- A crater on the Moon bears his name, honoring his contributions to science.
Conclusion
Sir Jagadish Chandra Bose’s legacy extends beyond scientific achievements. His curiosity, resilience, and passion continue to inspire generations of researchers and thinkers worldwide. ????????????
- J.B.S. Haldane: Life, Achievements, and Contributions to Genetics and Evolution
- Albert Einstein Biography, Education, Discoveries
- Dr. D.N. Wadia: Early Life, Career, Achievements, Contributions, and Legacy.
Note: This blog or artical is written on the basis of online research, news paper and AI tools. So, if there is any issue, please mail your feedback.
- Share:








